|
|
Operational Amplifiers Summary
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following is a summary of the different types of Operational Amplifiers and their configurations discussed in this tutorial section. |
|
|
|
|
|
The Operational Amplifier, or Op-amp as it is most commonly called, is an ideal amplifier with infinite Gain and Bandwidth when used in the Open-loop mode with typical d.c. gains of well over 100,000, or 100dB. |
|
|
The basic Op-amp construction is of a 3-terminal device, 2-inputs and 1-output. |
|
|
An Operational Amplifier operates from either a dual positive ( +V ) and an corresponding negative ( -V ) supply, or they can operate from a single DC supply voltage. |
|
|
The two main laws associated with the operational amplifier are that it has an infinite input impedance, ( Z∞ ) resulting in "No current flowing into either of its two inputs" and zero input offset voltage "V1 = V2". |
|
|
An operational amplifier also has zero output impedance, ( Z = 0 ). |
|
|
Op-amps sense the difference between the voltage signals applied to their two input terminals and then multiply it by some pre-determined Gain, ( A ). |
|
|
This Gain, ( A ) is often referred to as the amplifiers "Open-loop Gain". |
|
|
Closing the open loop by connecting a resistive or reactive component between the output and one input terminal of the op-amp greatly reduces and controls this open-loop gain. |
|
|
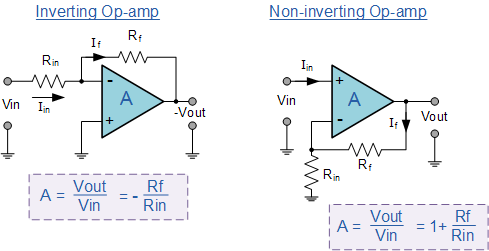
Op-amps can be connected into two basic configurations, Inverting and Non-inverting. |
|
|
|
|
|
The Two Basic Operational Amplifier Circuits
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
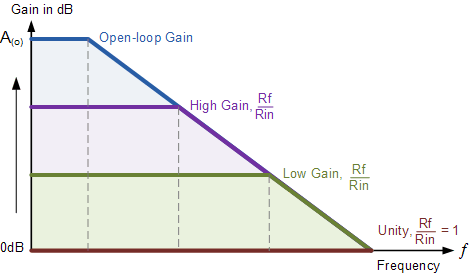
The Open-loop gain called the Gain Bandwidth Product, or (GBP) can be very high and is a measure of how good an amplifier is. |
|
|
Very high GBP makes an operational amplifier circuit unstable as a micro volt input signal causes the output voltage to swing into saturation. |
|
|
By the use of a suitable feedback resistor, ( Rƒ ) the overall gain of the amplifier can be accurately controlled.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gain Bandwidth Product
|
|
|
|
|
|
For negative feedback, were the fed-back voltage is in "anti-phase" to the input the overall gain of the amplifier is reduced. |
|
|
For positive feedback, were the fed-back voltage is in "Phase" with the input the overall gain of the amplifier is increased. |
|
|
By connecting the output directly back to the negative input terminal, 100% feedback is achieved resulting in a Voltage Follower (buffer) circuit with a constant gain of 1 (Unity). |
|
|
Changing the fixed feedback resistor ( Rƒ ) for a Potentiometer, the circuit will have Adjustable Gain. |
|
|
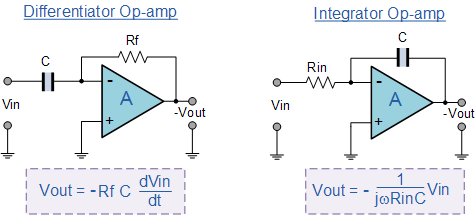
The Differential Amplifier produces an output that is proportional to the difference between the 2 input voltages. |
|
|
|
|
|
Differential and Summing Operational Amplifier Circuits
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|






